offer all kinds of Capacitors informations
-
Capacitors Blog Categories
-
Capacitors Blog Contact
- Fax #: 852 8208 6246
- Email : info@capacitors.hk
Voltage
Voltage is supplied by the battery (or power supply).
Voltage is used up in components, but not in wires.
We say voltage across a component.
Voltage is measured with a voltmeter, connected in parallel.
High stability is the important of a Quartz Crystal in Crystal Oscillators
One of the most important features of an oscillator is its Frequency Stability, or in other words its ability to provide a constant frequency output under varying conditions. Some of the factors that affect the frequency stability of an oscillator include: temperature, variations in the load and changes in the power supply. Frequency stability of the output signal can be improved by the proper selection of the components used for the resonant feedback circuit including the amplifier but there is a limit to the stability that can be obtained from normal LC and RC tank circuits. For very high stability a quartz crystal is generally used as the frequency determining device to produce another types of oscillator circuit known generally as Crystal Oscillators.
Suntan offer the high stability Quartz Crystal. So you don’t miss to know more about capacitors in Suntan. Welcome to send the inquire for us and call us to send the capacitors samples for your good view.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law is the linear proportionality between current and voltage that occurs for most conductors of electricity. A graph of voltage against current is a straight line. The gradient is the resistance.
The most well known form of Ohm's law is V=IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance. However there is another form of Ohm's law which often used by physicists that operates on a microscopic level, relating the current density J to the conductivity σ and the electric field, E.
To see how consider, the volume of material with faces of area A a distance I apart. With an e.m.f. V across the faces of the material:
the current is proportional to the voltage V
the current is proportional to the surface area A
and the current is inversely proportional to the distance I.
The current is therefore,
I = VAσ/I.
R = I/Aσ
The proportionality constant σ is the conductivity of the material.
V/I = |E|, and J = I/A in the direction of E so in general we have the constitutive relation.
J = σE
Power Rating for various Appliances in the Home
Electrical appliances used around the home are rated in Watts and electricity is sold by the kilowatt-hour. This is equivalent energy used by a device rated at 1000 W running for 1 hour, or 3.6 x 106 J. This is also the same energy as a Board of Trade Unit (BTU) (Not to be confused with the (British Thermal Unit) b.t.u. which describes the power of heating and cooling systems.)
To give some idea of how much energy electrical items consume the table below lists various electrical appliances and their power ratings.
| Appliance | Power Rating (W) |
| Water Heater | 4000 |
| Electric Cooker, Hob (one ring) | 2000 |
| Electric Cooker, Oven | 1500-2500 |
| Microwave Oven | 600-900 |
| Washing Machine | 2750 |
| Vacuum Cleaner | 800 - 1200 |
| Toaster | 1200 |
| Electric Kettle | 1200 - 2200 |
| Hair Dryer | 1000 |
| Plasma Television | 328 |
| LCD Television | 193 |
| CRT Television | 146 |
| Fridge | 110 |
| Incandescent Light Bulb | 40 - 100 |
| Computer | 78 |
| Laptop Computer | 65 |
| PlayStation II | 30 |
| Energy Efficient Light Bulb | 15 |
| Wireless Router | 7 |
| CRT Standby | 3 - 11 |
| Charging Mobile Phone | 3 |
| Solar Powered Calculator | 0.04 |
The actual cost of running all this equipment depends on how much a kilowatt of power costs and how long you use each appliance. However, it is clear that the most power hungry appliances are those used for heating things. What is surprising, is the high power consumption of LCD televisions in comparison to traditional CRTs.
Super Capacitors
Super Capacitors are capacitors which have the ability to store large amounts of charge, and therefore energy, in a very small volume. Energy storage is by means of static charge rather than of an electro-chemical process that is inherent to the battery. Applying a voltage differential on the positive and negative plates charges the super Capacitor. This concept is similar to an electrical charge that builds up when walking on a carpet. The super Capacitor was first conceived in 1957 but now research is focused on using these as a light weight power sources as an alternative for batteries. The super Capacitor crosses into battery technology by using special electrodes and some electrolyte.
Super Capacitors could find applications such as temporary back-up power supplies in the electrical power grid or providing the initial burst of energy to get electric cars moving.
Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are polarised and have low voltage ratings like electrolytic capacitors. They are expensive but very small so they are used where a large capacitance is needed in a small size such as mobile phones or laptop computers. These capacitors have increasingly become an important as the demand for ever smaller electronic gadgets has grown. Columbite-tantalite – coltan for short, the ore from which tantalum is refined is mined in Australia, Egypt.
You know the Quartz Crystal used in Crystal Oscillators?
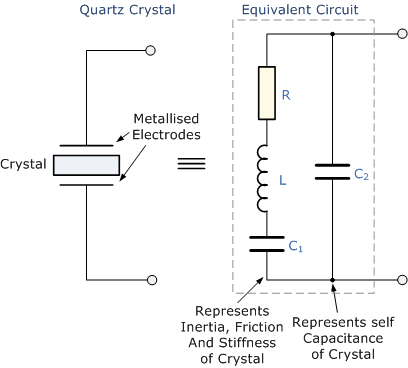
The Quartz Crystal used in Crystal Oscillators is a very small, thin piece or wafer of cut Quartz with the two parallel surfaces metallized to make the electrical connections. The physical size and thickness of a piece of Quartz Crystal is tightly controlled since it affects the final frequency of oscillations and is called the crystals "characteristic frequency". Then once cut and shaped the crystal can not be used at any other frequency. The crystals characteristic or resonant frequency is inversely proportional to its physical thickness between the two metallized surfaces. A mechanically vibrating crystal can be represented by an equivalent electrical circuit consisting of low Resistance, large Inductance and small Capacitance as shown below.
A case when a circuit tester
When a circuit tester, such as an analog meter set to measure resistance, is connected to a 10 microfarad (µF) electrolytic capacitor, a current will flow, but only for a moment. You can confirm that the meter's needle moves off of zero, but returns to zero right away.
When you connect the meter's probes to the capacitor in reverse, you will note that current once again flows for a moment. Once again, when the capacitor has fully charged, the current stops flowing. So the capacitor can be used as a filter that blocks DC current. (A "DC cut" filter.)
However, in the case of alternating current, the current will be allowed to pass. Alternating current is similar to repeatedly switching the test meter's probes back and forth on the capacitor. Current flows every time the probes are switched.
Brief summary of Capacitors
The capacitor's function is to store electricity, or electrical energy.
The capacitor also functions as a filter, passing alternating current (AC), and blocking direct current (DC).
This symbol ![]() is used to indicate a capacitor in a circuit diagram.
is used to indicate a capacitor in a circuit diagram.
The capacitor is constructed with two electrode plates facing eachother, but separated by an insulator.
When DC voltage is applied to the capacitor, an electric charge is stored on each electrode. While the capacitor is charging up, current flows. The current will stop flowing when the capacitor has fully charged.
Pay attention of the breakdown voltage
When using a capacitor, you must pay attention to the maximum voltage which can be used. This is the "breakdown voltage." The breakdown voltage depends on the kind of capacitor being used. You must be especially careful with electrolytic capacitors because the breakdown voltage is comparatively low. The breakdown voltage of electrolytic capacitors is displayed as Working Voltage.
The breakdown voltage is the voltage that when exceeded will cause the dielectric (insulator) inside the capacitor to break down and conduct. When this happens, the failure can be catastrophic.